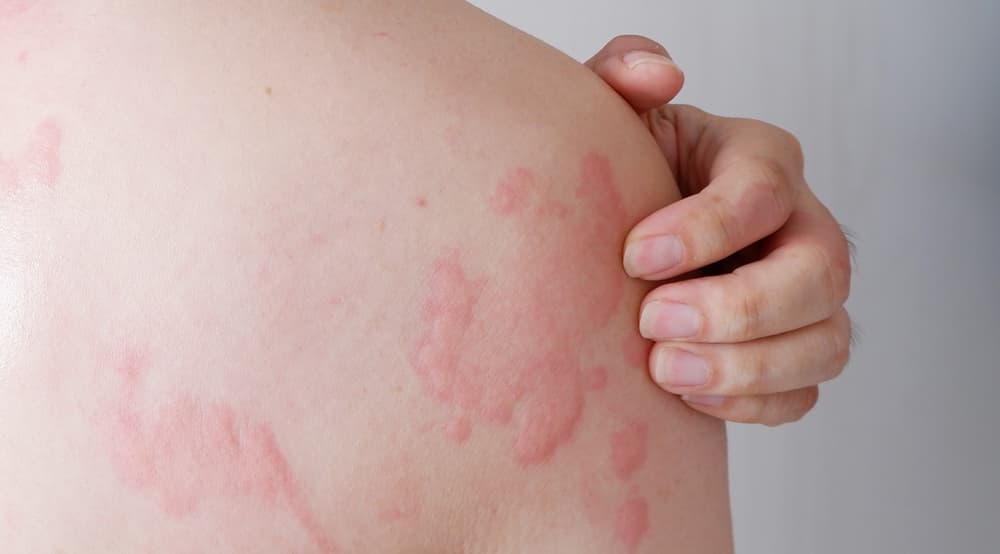
What causes hives?
Although hives can occur without reason, hives or urticaria can commonly happen because of an allergic reaction to any substance. When you have an allergic reaction, your body releases proteins called histamine or other chemicals into the blood.
This can cause tiny blood vessels called capillaries to dilate and leak fluid. The fluid then accumulates in the skin, causing inflammation and rashes, leading to common hive symptoms like itching, burning, and stinging.
Hives are often accompanied by angioedema, which causes swelling in the deeper skin tissues. When they occur around the mouth or throat, hives can cause severe symptoms and block the airways.
How can a person get hives?
Although there is no apparent reason why hives occur, a person can get hives because of an allergic reaction to:
Allergens
Hives can occur when someone eats, drinks, or touches anything that causes an allergic reaction. This is known as contact urticaria.
Acute hives can occur from allergic reactions to:
- Medications like antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or medicines for high blood pressure
- Plants like poison ivy
- Latex
- Seafood, nuts and eggs
- Additives in food, cosmetics
Physical triggers
Inducible hives can occur from physical triggers like:
- Extreme temperatures or changes in weather
- A high body temperature from sweating, hot showers, anxiety and exercise
- Rubbing or scratching of skin
- Exposure to sunlight
- Exposure to UV lights from tanning beds
- Pressure from a tight belt
- Vibrations and water on the skin in rare cases
Underlying health conditions
Chronic hives are caused by medical conditions such as:
- Bacterial infections like strep throat and urinary tract infections
- Viral infections, hepatitis B, common cold, flu
- Autoimmune conditions like type1 diabetes, celiac disease, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus
- Intestinal parasites like Giardia lamblia
- Autoimmune hypothyroidism
- Any other condition that causes inflammation in the blood vessels
What are the symptoms of hives?
Hives may appear as bug bites or raised bumps and show up in any area of the body. They may appear and disappear, change shapes and colors, and move around over some time.
The bumps may appear as follows:
- Red, pink, or skin-colored bumps that range from the size of a pinprick to several inches across
- Raised itchy bumps with clear edges
- Bumps with pale center when pressed, a process called blanching
Sometimes, hives may appear as:
- Thin, raised lines
- Blotches
- Tiny spots
Hives can appear on different body parts like:
- Face
- Arms
- Trunk
- Legs
Hives on legs or papular urticaria can occur because of insect or spider bites. In contrast, hives on the face can occur because of an allergic reaction that causes swelling in the mouth and throat, blocking airways, causing anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic reaction.
Hives are of three types based on how long you have the symptoms.
- Acute: Acute hives are allergic reactions to food, medications, or drinks that do not last beyond a few days to a week.
- Chronic: Chronic hives are spontaneous or idiopathic and are caused by bacterial or viral infections or from a medical condition like lupus. They usually last longer than six weeks but are not permanent.
- Inducible: Inducible hives are triggered by various physical factors, such as changes in body temperature or exposure to cold weather.
Are hives contagious?
Unlike most skin conditions, hives are not contagious. However, if you get hives from an underlying infection, that infection can be contagious.
What are the treatment options for hives?
Hives can be diagnosed through allergy tests that include:
- Blood tests: They check for specific antibodies in the blood. If you have too many antibodies in your blood, it may be because of hives and swelling.
- Skin tests: Skin prick or scratch tests are done where different allergens are tested on the skin. If your skin develops swelling or turns red in response to any allergen, you are allergic to that substance.
Hives can usually go away without treatment. To treat hives, your medical provider may recommend:
Allergy medications
Antihistamines are allergy medications that block the effect of histamine, a chemical in the skin that causes welts and other allergy symptoms. They also relieve skin itching and other symptoms of hives. Taken orally as a pill or used topically on the skin, antihistamines reduce the severity of allergic symptoms or make them disappear.
Based on the severity of the allergic reactions, your doctor may recommend allergy medications like cetirizine (Zyrtec) or diphenhydramine(Benadryl).
Allergy shots
Doctors recommend monthly injections to block allergic reactions from chronic hives that are difficult to treat. Allergy shots work by blocking the immune system from making too much IgE.
Oral steroids
Hive symptoms that do not respond to antihistamines or topical steroids are treated by oral steroids like corticosteroids and prednisone.
Epinephrine injections
Hives on the face can cause swelling of the mouth and throat, wheezing, shortness of breath, and low blood pressure. A severe allergic reaction can cause anaphylaxis, a life-threatening reaction requiring immediate epinephrine injections to open a swollen airway.
Hydroxychloroquine
Where chronic hives develop from an autoimmune disease, hydroxychloroquine, an antimalaria drug, is prescribed for three or more months.
Cyclosporin
It is an immunosuppressant drug used to treat chronic hives. It can have serious side effects when taken for too long.
If you are curious about the causes, symptoms, and how to get lasting relief from annoying hives, here is a comprehensive video from Dr. Nerissa D'Silva, MD, Allergist Houston ENT, Sugar Land office, that you can watch.
How to Get Rid of Hives
In addition to medical treatments, you can try home remedies to soothe inflammation and ease hives symptoms.
You can:
- Take a cool bath or shower;
- Apply OTC anti-itch cream or lotion;
- Wear loose-fitting clothes from natural fibers to avoid skin irritation;
- Apply hypoallergenic creams and lotions to keep your skin hydrated and prevent allergies;
- Use a cool compress on hives to relieve the symptoms.
To lower the incidence of hives, you must avoid the known triggers that cause them.
Schedule an appointment with Houston ENT & Allergy
Hives are your body’s response to the allergens that trigger the allergy symptoms. The best way to treat allergic reactions is to identify the triggers and take steps to prevent them.
If you are prone to allergic symptoms and develop itching and swelling, you need specialized treatment supervised by a physician in a facility with proper staff and equipment to identify and treat the hives symptoms.
Our allergists at Houston ENT & Allergy are committed to understanding your concerns and offering tailor-made treatments to treat your hive-related allergy issues. Our highly trained specialists can treat hives symptoms and prevent new allergy conditions in you or your loved ones.
Schedule an appointment here or call us at (281) 649-7000. We have nine convenient locations in the Houston area.